
Real estate investments are popular due to several factors. These include the steady cash flow generated by rental properties, the potential for appreciation in property value, the diversification benefits it offers to investment portfolios, the tax advantages associated with real estate investments, the ability to act as a hedge against inflation, the leverage opportunity it provides, the tangible nature of real estate assets, and the long-term stability historically associated with the real estate market.
How to Make Money in Real Estate
Making money in real estate can be a profitable venture if done correctly. Here are several strategies that can help you make money in real estate:
1. Buy and Hold
Purchase properties with long-term potential for appreciation and rental income. This strategy involves finding properties in desirable locations and holding onto them for an extended period. As property values increase over time, you can generate income from rental payments and sell the property at a profit in the future.
While the “Buy and Hold” strategy can be lucrative, it’s important to conduct thorough due diligence before purchasing a property. Factors such as location, market conditions, property management, and potential rental income should all be carefully evaluated. Additionally, regular property maintenance and staying updated on market trends will help you maximize your returns and maintain the value of your investment over time.
Median Sales Price of Houses Sold for the United States
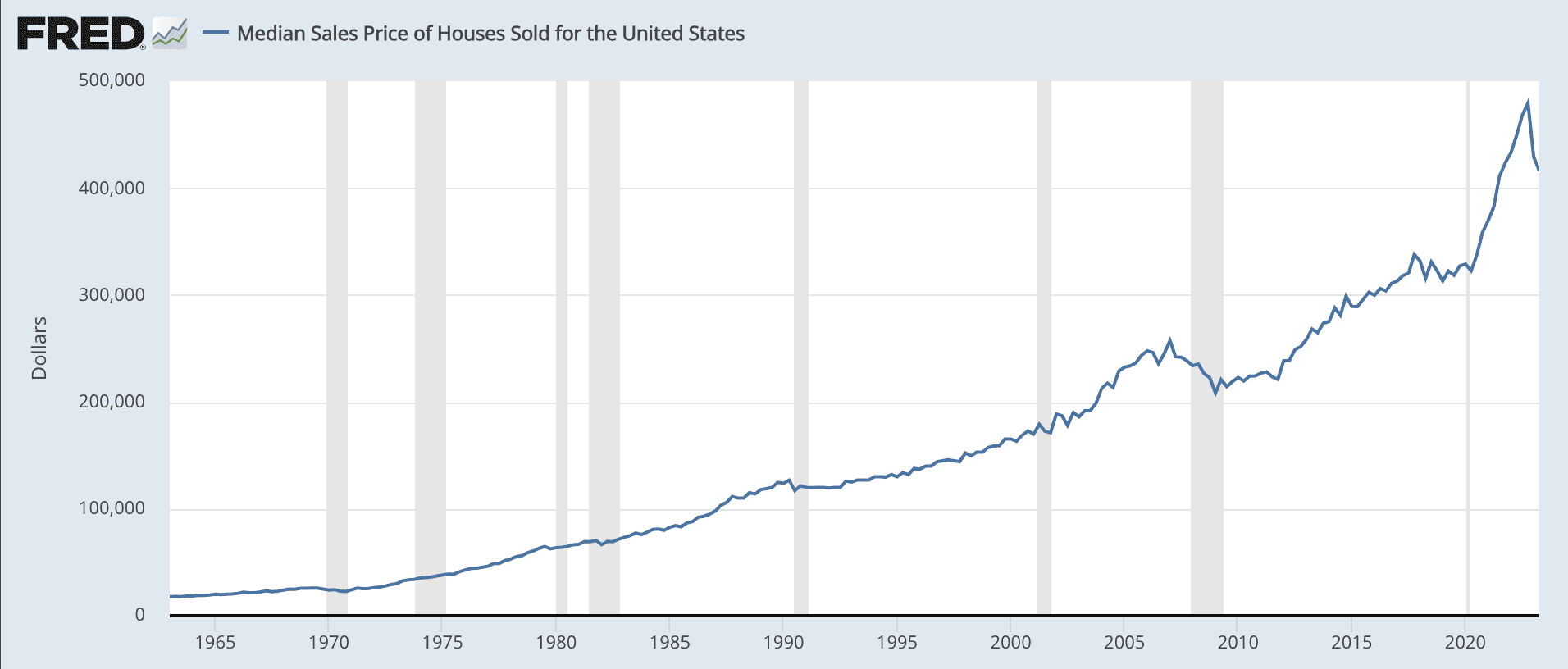
Overall, the “Buy and Hold” strategy offers a long-term approach to wealth accumulation in real estate, combining appreciation, rental income, tax benefits, and portfolio diversification. By investing wisely and managing your properties effectively, you can make money and build wealth through this strategy.
2. Fix and Flip
Buy properties that require renovations or improvements, with the intention of selling them quickly at a higher price. This strategy requires careful market research, knowledge of construction and renovation costs, and a keen eye for profitable opportunities. Flipping properties can be lucrative, but it comes with risks, such as unexpected expenses during renovations and market fluctuations.
3. Rental Properties
Invest in residential or commercial properties and generate income through renting. This strategy involves buying properties with good rental potential, such as in high-demand areas or near schools and businesses. With proper management, rental properties can provide consistent monthly income.
Let’s expand on some of the key points and explore additional factors that can make investing in rental properties even more interesting:
1) Location, Location, Location! When it comes to rental properties, the location can greatly impact your investment success. Consider properties in popular destinations, areas with high rental demand, and neighborhoods experiencing growth and development. Investing in properties near universities, vibrant city centers, or in emerging neighborhoods can provide exciting opportunities for attracting quality tenants and maximizing rental income.
2) Short-Term Rentals and Airbnb. Another interesting aspect of rental property investing is the option to explore short-term rentals, such as Airbnb. This allows you to cater to a different type of tenant and potentially earn higher rental rates. Short-term rentals can be especially attractive in tourist destinations or areas with high demand for temporary accommodations. They offer the flexibility to rent out the property on a daily or weekly basis, giving you the opportunity to maximize your rental income during peak seasons.
3) Renovations and Value-Add Opportunities. Investing in fixer-upper properties or those with renovation potential can be an exciting way to increase the value of your rental property. By improving the property’s aesthetics, functionality, or amenities, you can attract higher-quality tenants and potentially command higher rental rates. Renovations can also have a positive impact on property appreciation, enabling you to build equity more rapidly.
4) Technology and Property Management Tools. The advancement of technology has revolutionized the way rental properties are managed. Property management tools, online platforms, and automated systems can streamline processes, making the management of rental properties more efficient and convenient. From online rent collection systems to smart home devices that enhance security and energy efficiency, incorporating technology into your rental property can be both interesting and beneficial.
5) Vacation and Luxury Rentals. In addition to traditional long-term rentals, investing in vacation or luxury rentals can be a fascinating endeavor. These types of properties cater to high-end clientele looking for unique and memorable experiences. By targeting niche markets or prime vacation destinations, you can tap into a lucrative segment of the rental market and potentially earn premium rental income.
7) Green and Sustainable Properties. Investing in eco-friendly and sustainable rental properties can be a compelling way to align your investment strategy with your values. These properties focus on energy efficiency, reducing carbon footprints, and incorporating sustainable building practices. In addition to attracting environmentally conscious tenants, green properties often qualify for tax incentives and rebates, providing additional financial benefits.
8) International Real Estate. If you’re seeking a truly exciting investment opportunity, consider looking beyond your local market and exploring international real estate. Investing in rental properties in popular tourist destinations, emerging economies, or locations with attractive tax incentives can be an intriguing way to diversify your real estate portfolio and potentially tap into unique market dynamics and rental demand.
9) Community Impact and Social Responsibility. Rental properties provide an opportunity to make a positive impact on the community. Investing in affordable housing or properties in underserved areas can contribute to housing accessibility and help address social issues. By aligning your investment strategy with social responsibility, you can create a sense of purpose while generating financial returns.
4. Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
Consider investing in REITs, which are companies that own and operate income-generating real estate. REITs allow you to invest in real estate without the need for direct property ownership. By purchasing shares in a REIT, you can earn dividends and benefit from the appreciation of the real estate portfolio. Here are some key aspects of REITs and how they can be used to make money in real estate:
1) Diversification. Investing in REITs allows for diversification within the real estate sector. REITs typically own and manage a portfolio of different types of properties, including commercial buildings, residential complexes, industrial parks, hotels, and more. By investing in REITs, you can gain exposure to a diverse range of real estate asset classes, reducing the risk associated with holding a single property.
2) Passive Income. REITs generate income primarily from rental income collected from their properties. They are required by law to distribute a significant portion of their taxable income to shareholders in the form of dividends. This means that investors can potentially earn regular passive income by owning shares in REITs. Dividends earned from REIT investments are usually higher compared to dividends from other stocks, largely due to the requirement that REITs distribute a significant portion of their income to shareholders.
3) Professional Management. One of the advantages of investing in REITs is that the properties are professionally managed. REITs employ experienced real estate professionals who handle property management, maintenance, tenant relations, and other operational aspects. This allows investors to benefit from the expertise of professionals, without the need for hands-on management of individual properties.
4) Liquidity. Real estate investments are often considered illiquid, as it can take time to sell a property. However, investing in publicly-traded REITs provides liquidity. REITs are listed and traded on major stock exchanges, allowing investors to buy and sell shares easily. This liquidity feature makes REITs more flexible compared to direct property ownership, as you can quickly adjust your investment portfolio based on market conditions or personal circumstances.
5) Potential for Capital Appreciation. While the primary focus of REITs is generating rental income, they can also provide opportunities for capital appreciation. If the value of the underlying real estate assets held by a REIT increases over time, the value of the REIT’s shares can appreciate. This allows investors to benefit from both regular dividend payments and potential capital gains when selling their shares.
6) Access to Large-Scale Properties. Another advantage of investing in REITs is gaining access to large-scale properties that may be beyond individual investors’ reach. REITs can acquire and manage properties of significant value, including landmark buildings and commercial properties in prime locations. By investing in REITs, you can indirectly participate in the ownership of prestigious properties that might not be available for individual ownership.
7) Lower Barriers to Entry. Investing in individual properties often requires substantial capital, loan qualifications, and a deep understanding of the real estate market. REITs, on the other hand, offer an avenue for smaller investors to participate in the real estate market with relatively lower investment amounts. As REITs pool funds from multiple investors, individuals with smaller capital can still gain exposure to a diversified portfolio of real estate assets.
8) Tax Advantages. REITs can provide tax advantages to investors. By distributing a significant portion of their taxable income to shareholders, REITs often pay little or no corporate income taxes. This enables investors to receive the majority of the income in the form of dividends, potentially resulting in favorable tax treatment. However, it’s important to consult with a tax professional to understand the specific tax implications based on your jurisdiction and individual circumstances.
9) Investment Options. REITs come in various types, providing investors with options based on their investment goals and preferences. For example, equity REITs primarily own and operate income-generating properties, while mortgage REITs invest in real estate debt. There are also specialized REITs that focus on specific segments such as healthcare, hospitality, or industrial properties. By choosing the right type of REIT, investors can align their investment strategy with specific market trends or sectors they find appealing.
10) Professional Guidance. Investing in REITs allows investors to leverage the expertise of professional fund managers and real estate specialists. Many financial advisors are well-versed in REIT investments and can provide guidance on selecting suitable REITs based on an investor’s risk tolerance, investment timeline, and financial goals. Professional expertise can help optimize investment decisions, potentially leading to better returns and risk management.
While investing in REITs can be a viable way to make money in real estate, it is important to conduct thorough research and due diligence. Consider factors such as the REIT’s track record, its portfolio composition, historical performance, management team, and the economic conditions affecting its underlying properties. REITs, like any investment, carry risks such as market fluctuations and interest rate changes that can affect their profitability. It’s advisable to consult with a financial advisor or real estate professional who can provide personalized guidance based on your individual circumstances and investment objectives.
5. Wholesale Properties
This strategy involves purchasing properties at a discounted price and then selling them to other investors for a profit. Here’s a closer look at how wholesale properties work and how you can make money with this approach:
1) Finding Distressed Properties. The first step in wholesale real estate is finding distressed properties that can be purchased below market value. Distressed properties are typically in poor condition, facing foreclosure, or owned by motivated sellers who are looking to sell quickly. Some common sources for finding distressed properties include real estate auctions, foreclosure listings, short sales, and networking with local real estate agents and other investors.
2) Negotiating a Low Purchase Price. Once you identify a distressed property, the key to making money with wholesaling is to negotiate a purchase price significantly below the property’s market value. This requires negotiation skills, market knowledge, and the ability to assess the potential renovation costs the property may need. The goal is to secure a low enough purchase price to leave room for a profit when selling to another investor.
3) Assigning the Contract. Instead of actually closing on the property, wholesalers often assign their purchase contract to another investor. This means that the original wholesaler finds a buyer who is willing to take over the contract and close on the property. The wholesaler then receives an assignment fee from the buyer, which is typically a percentage of the purchase price. The buyer, in turn, assumes the rights and responsibilities of the original contract.
4) Developing a Network of Investors. Building a network of real estate investors who are interested in buying wholesale properties is crucial for success in wholesaling. Attend local real estate investment club meetings, network online, and reach out to experienced investors to create relationships. By having a network of potential buyers, you can quickly assign contracts and close deals, maximizing your profits.
5) Rehabbing and Flipping. In some cases, wholesalers may choose to take on the responsibility of rehabbing distressed properties before selling them. This strategy involves purchasing the property, renovating it, and then reselling it at a higher price. By improving the property’s condition and appearance, you can increase its market value and potential selling price. However, this approach requires more capital, expertise, and time compared to simple assignments.
6) Understanding Market Dynamics. To be successful in wholesale real estate, it’s essential to have a solid understanding of the local real estate market and the factors that drive property values. Familiarize yourself with market trends, comparable property sales, rental rates, and other relevant data. This knowledge will help you accurately assess the potential profit margins and negotiate favorable deals. Stay updated on changes in zoning laws, development plans, and economic indicators that may impact property values.
7) Conducting Due Diligence. Before entering into any wholesale property deal, it’s crucial to conduct thorough due diligence. This includes researching the property’s title, assessing its physical condition, estimating repair costs, and understanding any legal or financial obligations associated with the property. Failing to complete proper due diligence can lead to unforeseen expenses or legal issues that can eat into your profits.
8) Building Trust and Reputation. Reputation is key in the real estate industry. Building a trustworthy and reliable reputation is essential for attracting both distressed property sellers and buyers for your wholesale deals. Delivering on promises, being transparent, and maintaining ethical practices are crucial for establishing credibility and attracting repeat business.
9) Managing Risks. As with any investment strategy, wholesaling real estate involves risks. Fluctuating property values, unforeseen renovation costs, legal issues, and market volatility are just a few factors that can affect profitability. It’s important to assess and manage these risks effectively by diversifying your deals, maintaining a financial buffer, and having a contingency plan in case of obstacles or unfavorable market conditions.
Wholesaling properties can provide an opportunity to generate quick profits in real estate without the need for substantial upfront capital. However, like any investment strategy, success re
6. Real Estate Development
Invest in developing properties by purchasing land and building or renovating properties. This strategy requires in-depth knowledge of zoning regulations, construction costs, and market demand. Real estate development can be profitable but carries higher risks due to the capital and time involved in the process. Here’s a closer look at how real estate development works and how you can make money with this approach:
1) Identifying Profitable Opportunities. Successful real estate development starts with identifying profitable opportunities in the market. This involves conducting market research, analyzing demographic trends, assessing supply and demand dynamics, and identifying areas with growth potential. These insights help developers identify properties or areas where there is a demand for new real estate projects.
2) Acquiring Property. Once a profitable opportunity is identified, the next step is to acquire the property. Developers may purchase land, underutilized properties, or even existing buildings with the potential for renovation or redevelopment. Negotiating a favorable purchase price is crucial to ensure profitability.
3) Conducting Feasibility Studies. Before moving forward with a development project, developers conduct feasibility studies to evaluate the financial viability of the project. This analysis includes assessing construction costs, estimating the potential sales or rental income, evaluating the market demand, and considering any regulatory or zoning restrictions. It helps developers determine if the project is economically feasible and can generate the desired return on investment.
4) Securing Financing. Real estate development projects often require significant capital investments. Developers secure financing through various sources, including banks, private investors, joint ventures, or syndications. Effective financial management, including budgeting, cost control, and monitoring cash flow, is essential to ensure the project remains economically viable.
5) Obtaining Necessary Approvals. Real estate development projects often require various permits, licenses, and approvals from local authorities and regulatory bodies. Developers must navigate zoning restrictions, environmental assessments, building codes, and other regulatory requirements. This process requires coordination with government agencies, architects, engineers, and other professionals to ensure compliance.
6) Designing and Planning. The design and planning phase encompasses creating the vision for the development project. Developers work with architects, engineers, and urban planners to design buildings and layout the infrastructure, taking into account factors such as functionality, aesthetics, sustainability, and market demand. An enticing and well-designed project can add value and attract buyers or tenants, increasing the potential for profit.
7) Managing Construction. Once the design and planning phase is complete, construction begins. Developers oversee the construction process, ensuring that quality standards are met, timelines are followed, and costs are controlled. Effective project management and communication with contractors and subcontractors are crucial to minimize delays and cost overruns.
8) Marketing and Sales. As the development nears completion, developers focus on marketing and sales to attract potential buyers or tenants. Effective marketing strategies may include advertising, signage, online listings, and engaging with real estate agents or brokers. Developers aim to sell or lease the units or properties at a price that yields a profit, taking into account the expenses incurred during the development process.
9) Maximizing Profit. Profit in real estate development can come from various avenues. Developers may sell completed properties to buyers or investors at a higher price than their initial investment, generating capital gains. Rental income from commercial or residential units can provide a steady stream of cash flow. Some developers also make money by retaining an ownership stake in the development and earning income from asset management or property management fees.
10) Mitigating Risks. Real estate development involves inherent risks, including market volatility, regulatory hurdles, construction delays, or unexpected expenses. Developers mitigate risks by conducting thorough due diligence, working with experienced professionals, securing appropriate insurance coverage, and having contingency plans in place. Diversifying investments across different projects and markets can also help spread risk.
11) Continuous Learning and Adaptation. Real estate development requires staying informed about market trends, design innovations, construction techniques, and changing regulations. Successful developers continually educate themselves, network with industry professionals, and adapt their strategies to stay competitive and take advantage of emerging opportunities.
Real estate development can be a highly rewarding endeavor, but it is not without its challenges. Successful developers possess a combination of market knowledge, financial acumen, project management skills, and creativity. They understand how to identify profitable opportunities, mitigate risks, and deliver high-quality projects that meet market demand. By approaching real estate development strategically and considering market trends, demographics, and lifestyle preferences, developers can increase their chances of making money in this field.
7. Real Estate Syndication
Join forces with other investors to pool resources and invest in larger real estate projects. This strategy allows you to access larger properties or projects that may be beyond your individual capacity. By partnering with experienced investors, you can leverage their expertise while sharing the risks and potential returns.
Here’s a closer look at how real estate syndication works and how it can be a profitable endeavor:
1) Partnership Structure. Real estate syndication typically involves the formation of a limited liability company (LLC) or a limited partnership (LP). The general partner, or sponsor, is responsible for sourcing the deal, conducting due diligence, securing financing, and overseeing the project’s day-to-day operations. Limited partners provide the majority of the capital investment but have limited liability and a passive role in decision-making.
2) Access to Larger-scale Investments. Syndication allows individual investors to participate in real estate projects that would typically be beyond their financial reach. By pooling resources, investors can access larger-scale investments, such as multi-family properties, office buildings, retail centers, or even development projects. This diversification of investment types and geographical locations can potentially reduce risk and increase the chances of generating higher returns.
3) Expertise and Experience. Real estate syndication offers investors the opportunity to leverage the expertise and experience of the general partner or sponsor. The sponsor’s knowledge of the market, access to deal flow, and ability to negotiate favorable terms can contribute to the success of the investment. This is particularly valuable for investors who may be new to real estate or lack specialized knowledge in certain property types or markets.
4) Risk Mitigation. Participating in a real estate syndication can help spread the risk among multiple investors. Instead of investing in a single property or project, investors can diversify their investments across different properties and markets. This diversification can mitigate the risk associated with market fluctuations, tenant turnover, or unforeseen events such as natural disasters.
5) Cash Flow and Passive Income. Real estate investments through syndication can provide investors with consistent cash flow and passive income. Rental income from commercial or residential properties is often distributed to investors on a regular basis, such as quarterly or annually. This stream of income can be an attractive aspect of real estate syndication, particularly for those seeking passive investment opportunities.
6) Capital Appreciation. Real estate syndication also offers the potential for capital appreciation. As the property value increases over time, investors may realize a profit when the property is sold or refinanced. The sponsor’s expertise in finding undervalued properties, adding value through renovations or operational improvements, and positioning the property for sale can drive the property’s appreciation and generate attractive returns for investors.
7) Limited Liability and Tax Benefits. Limited partners in a syndication structure typically have limited liability. Their personal assets are protected in the event of any lawsuits or property-related liabilities. Additionally, real estate syndication can offer tax benefits. Investors may be able to take advantage of tax deductions, favorable depreciation schedules, and sometimes even pass-through taxation, where profits flow through to individual investors’ tax returns.
8) Exit Strategy and Liquidity. One of the key aspects of real estate syndication is establishing an exit strategy for investors. This could involve selling the property at a predefined timeline or refinancing to return capital to investors. The sponsor’s expertise is crucial in executing the exit strategy efficiently and maximizing returns for investors. However, it’s important to note that real estate investments are typically considered illiquid, meaning that it may take time to sell or refinance the property and return the investors’ capital.
9) Ongoing Communication and Reporting. Effective communication between the general partner and limited partners is vital in a real estate syndication. Regular updates, financial statements, and investor reports provide transparency and keep investors informed about the progress and performance of the investment. This transparency helps build trust and confidence among all parties involved.
Real estate syndication can be a rewarding investment strategy, but it’s important to carefully evaluate potential investments and consider the track record and experience of the general partner. Investors should conduct thorough due diligence, review the investment structure and terms, and ensure alignment of interests between the sponsor and limited partners. Engaging the services of legal and financial professionals who specialize in real estate syndication can provide valuable guidance throughout the investment process.
8. Lease Options
Enter into lease agreements with the option to purchase the property at a later date. With this strategy, you can generate income from tenants while having the flexibility to buy the property if favorable conditions arise. Lease options can be beneficial if you expect property values to increase or if you need time to secure financing. Here’s a closer look at how lease options work and how they can be a profitable endeavor:
1) Agreement Structure. A lease option typically consists of two agreements: a lease agreement and an option agreement. The lease agreement establishes the terms and conditions of the rental period, including the monthly rent, lease duration, and responsibilities of the tenant. The option agreement provides the tenant with the right, but not the obligation, to purchase the property at a predetermined price within a specific timeframe.
2) Rent Premium. In a lease option, the tenant-buyer often pays a non-refundable fee, referred to as the option fee or rent premium, to the lessor. This fee serves as consideration for the option to purchase the property in the future. The option fee is typically higher than the market rent and is often non-refundable. The rent premium provides the lessor with immediate income and compensation for granting the tenant the option to purchase the property.
3) Price and Term Negotiation. The purchase price and the duration of the lease option are negotiated between the lessor and tenant-buyer at the outset of the agreement. The purchase price is typically set at a higher amount than the current market value to account for potential appreciation during the lease option period. The term of the lease option is also agreed upon and can range from a few months to several years, allowing the tenant-buyer sufficient time to secure financing or improve their financial situation.
4) Income Generation. Lease options can be a source of consistent rental income for the lessor. The monthly rent payments received from the tenant provide the lessor with regular cash flow. Additionally, the non-refundable rent premium paid by the tenant at the beginning of the lease option period provides additional income upfront.
5) Capital Appreciation. One of the key advantages of lease options for the tenant-buyer is the potential for capital appreciation. By agreeing on a purchase price at the beginning of the lease option period, the tenant-buyer can benefit if the property value increases during their occupancy. They have the option to purchase the property at the predetermined price, even if the market value has risen. This potential for capital appreciation is an attractive aspect of lease options for tenant-buyers looking to build equity over time.
6) Property Improvements. Lease options often allow tenant-buyers to make improvements to the property during the lease period. This can benefit both the tenant-buyer, who can customize the property to their preferences, and the lessor, who can potentially benefit from the added value created by the improvements. However, it is essential to establish clear guidelines and obtain written consent from the lessor before making any significant modifications.
7) Risk Mitigation. Lease options can help mitigate risks for both parties. For the tenant-buyer, they can “test drive” the property and the neighborhood before committing to a purchase. This allows them to assess whether the property meets their needs and if they are comfortable with the area. For the lessor, the non-refundable rent premium provides some compensation if the tenant-buyer decides not to exercise their option to purchase the property.
8) Flexibility and Negotiation. Lease options offer flexibility and negotiation options for both parties. If the tenant-buyer decides not to exercise their option, the lessor can keep the rent premium and look for another potential tenant-buyer. Conversely, if the tenant-buyer wants to exercise their option but encounters difficulties securing financing, there may be room for negotiation on the terms of the financing or an extension of the lease option period.
9) Proper Documentation and Legal Considerations. Lease options must be properly documented to protect the interests of both parties. It is crucial to consult with legal professionals experienced in real estate transactions to draft the lease agreement and option agreement. These documents should clearly outline the rights, responsibilities, and obligations of each party involved. Additionally, it is important to comply with local laws and regulations governing lease options.
While lease options can be a profitable endeavor in real estate, it is essential to carefully evaluate potential tenant-buyers and ensure that the terms and conditions of the agreement are legally binding and enforceable. Engaging the services of real estate professionals, such as attorneys and real estate agents, can provide valuable guidance throughout the process and help ensure a successful lease option transaction.
9. Tax Liens and Deeds
Invest in tax liens or tax deeds, which are properties that have unpaid property taxes. These methods involve purchasing properties with outstanding tax debts from the government or local authorities. Here’s an overview of tax liens and tax deeds and how they can be profitable:
1) Tax Liens. When property owners fail to pay their property taxes, the government or local authorities place a lien on the property. Tax liens are a claim against the property’s value to secure the unpaid tax debt. Investors can purchase tax liens at auctions, paying the outstanding tax debt on behalf of the property owner. In return, the investor receives a certificate that represents the lien against the property. Here’s how tax liens can be profitable:
- Interest Income. When an investor purchases a tax lien, they become the lienholder and have the right to collect the delinquent tax debt plus interest from the property owner. The interest rates on tax liens can vary, but they tend to be higher than traditional investment options. The interest earned on tax liens can provide significant income to the investor.
- Redemption Period. After acquiring a tax lien, the property owner is typically given a redemption period to repay the tax debt plus interest. If the property owner redeems the lien by paying the outstanding debt within this period, the investor receives the full amount of their investment plus interest. If the property owner fails to redeem the lien, the investor may have the opportunity to foreclose on the property and obtain ownership through a tax deed.
- Property Acquisition. In cases where the property owner doesn’t redeem the tax lien, the investor may have the opportunity to foreclose on the property and obtain ownership through a tax deed. This can allow the investor to acquire the property at a discounted price. The investor can then decide to sell the property, rent it out for passive income, or utilize other real estate investment strategies.
2) Tax Deeds. In some jurisdictions, instead of selling tax liens, the government or local authorities hold tax deed auctions, where they sell properties with outstanding tax debts. Investors can bid on these properties at an auction and acquire ownership directly through a tax deed. Here’s how tax deeds can be profitable:
- Lower Acquisition Cost. Tax deed auctions often provide opportunities to acquire properties at significantly discounted prices. Bidders can potentially purchase properties for a fraction of their market value, allowing them to profit when reselling or renting out the properties.
- Potential Price Appreciation. Depending on the location and condition of the property, investors can see the value of the property appreciate over time. They can then sell the property at a higher price, generating a profit.
- Immediate Equity. In some cases, properties sold through tax deed auctions have existing equity, meaning the current market value of the property is higher than the auction price. By acquiring the property through a tax deed auction, investors can gain immediate equity, which can be realized when selling or refinancing the property.
3) Research and Due Diligence. To succeed in tax liens and tax deeds, thorough research and due diligence are essential. Here are some key considerations:
- Property Evaluation. Before bidding on a tax lien or tax deed, it’s crucial to evaluate the property thoroughly. Assess its condition, location, market demand, and potential for value appreciation.
- Title Search. Conduct a title search to identify any existing liens, mortgages, or other encumbrances on the property. A clear title is necessary for a successful real estate investment.
- Auction Rules and Procedures. Understand the rules and procedures of tax lien and tax deed auctions in the specific jurisdiction you intend to invest in. Ensure you comply with all requirements to participate in the auction successfully.
- Redemption Periods and Foreclosure Laws. Familiarize yourself with the redemption periods and foreclosure laws in your desired location. Different jurisdictions have varying redemption periods, which can impact the timing and outcome of your investment.
- Local Market Knowledge. Gain a good understanding of the local real estate market trends, property values, rental demand, and potential for price appreciation. This knowledge will help you make informed investment decisions.
4) Professional Guidance. Consider working with professionals, such as attorneys, real estate agents, or tax professionals, to guide you through the process. Their expertise can help ensure compliance with local laws, minimize risks, and maximize your chances of success.
Both tax liens and tax deeds can provide opportunities for profitable real estate investments. However, it’s important to note that these strategies involve risks, and it’s essential to thoroughly understand the specific rules and regulations in the jurisdictions you plan to invest in. Conducting proper due diligence, understanding the potential pitfalls, and seeking professional advice will increase your chances of making successful and profitable investments in tax liens and tax deeds.
10. Crowdfunding
Participate in real estate crowdfunding platforms that allow various investors to contribute smaller amounts of money towards larger real estate projects. It provides an opportunity to diversify investments and access projects that may otherwise be out of reach. However, thorough due diligence is necessary to assess the credibility and potential returns of crowdfunding opportunities.
Before investing in real estate crowdfunding, it’s important to consider the following:
- Research and Due Diligence. Thoroughly research and understand the real estate crowdfunding platform, the projects available, and the risks associated with each investment opportunity. Conduct due diligence on the platform’s track record, developers, property evaluations, market analysis, and projected returns.
- Investment Horizon. Real estate investments typically require a long-term commitment. Evaluate your investment horizon and determine if you can afford to tie up your capital for the expected duration of the investment.
- Risk Factors. Real estate investments involve inherent risks, such as market fluctuations, economic downturns, unexpected costs, and project delays. Assess your risk tolerance and ensure it aligns with the risk profile of the projects you consider investing in.
- Platform Fees. Crowdfunding platforms may charge fees for their services. Understand the fee structure and evaluate how these fees might impact your potential returns.
- Regulatory Compliance. Real estate crowdfunding is subject to securities regulations and laws. Ensure that the crowdfunding platform you choose operates within the legal framework of your jurisdiction.
Remember, real estate investing is not without risks. It is crucial to conduct thorough research, have a solid financial plan, and work with professionals, such as real estate agents, lawyers, and accountants, to maximize your chances of success. Additionally, stay updated with market trends and economic indicators to make informed investment decisions.